Bitcoin Fee And Transaction Approval Issue; Everything You Need To Know
When Satoshi Nakamoto, The Anonymous Creator Of Bitcoin, Introduced This Revolutionary Phenomenon, He Cited High Transaction Fees As One Of The Problems Of Traditional Financial Systems.
With the expansion of the Bitcoin network, Bitcoin Fee can transfer millions of dollars in multi-dollar fees anywhere globally in an hour or less.
However, if you want to buy a cheap product like a cup of coffee with the Bitcoin network, the fee you have to pay will probably be more than the cost of coffee. Can this be considered a weakness of the Bitcoin network?
Bitcoin(Transaction Fee), sometimes called extraction fee, is the cost that Bitcoin users must pay to submit a transaction. This fee is paid to miners or extraction pools. Bitcoin is awarded.
The significant thing about the Bitcoin fee is that the transaction fee is set in a very new way and completely free and competitive way; This means that the high transaction amount does not necessarily increase the commission.
Setting a sufficient fee allows users to prioritize their transaction over other transactions and enter it faster—blockchain bitcoin. When choosing transactions to build blocks, miners are looking for the transaction that pays the most.
Therefore, if the fee you set for your transaction is not sufficient, the transaction may have to wait for approval for a long time.
Before reading this article, it is important to know that you do not have to set a fee manually to perform bitcoin transactions. All of today’s Bitcoin wallets can automatically set the standard fee for each transaction based on the average network fee and deduct it from your balance.
In this article, with the help of an essay Compiled from the 99Bitcoins training website, we review the basics of Bitcoin fees and try to provide a comprehensive explanation of Bitcoin transaction fees.
By reading this article, you will learn:
-
What is the Bitcoin fee, and on what basis is it calculated?
-
What effect does a change in Bitcoin transaction fees have on the speed of transaction approval?
-
And What is the minimum fee we have to pay to confirm a transaction?
-
How to change the transaction fee in Bitcoin wallets?
-
What resources should we refer to determine the commission rate and the appropriate time to complete the transaction?
-
What are some ways to reduce the cost of bitcoin transactions?
Follow us to the end of this article to answer these questions.
What is the Bitcoin transaction fee?
The transaction fee is when the bitcoin owner pays the miners to transfer their bitcoin assets to another bitcoin address. Bitcoin wallets set the fee for each transaction automatically based on network traffic, But many wallets also allow users to adjust their transaction fees according to transaction priority manually.
But to better understand the details of transaction fees, we must first know what happens when a bitcoin is transferred to another address? Transferring bitcoins from one address to another is a process that involves the following steps:

1. Announcing a transaction to the network and validating it
After you have signed a transaction in your wallet and your wallet software has sent it to the network, all computers with a copy of the Bitcoin blockchain check the transaction’s validity. In bitcoin and digital currencies, these computers are called NodeThis process is known as validation. At this point, the nodes review the bitcoin transaction history to make sure that the bitcoins you intend to spend actually belong to you and have not been spent before.

2. Sending the transaction to the memory pool
After confirmation, the transaction is sent to the memory pool or Mempool. An enclosure is a type of “waiting room” in which transactions wait to be selected by miners and registered in a block (packages containing the transaction). At this point, the transaction “unapproved» (unconfirmed) or “no confirmation» (0Confirmation) is evaluated. In fact, in simple terms, the transactions (in blocks) are not yet closed at this stage.

3. Block Registration and Transaction Verification
Whenever a miner selects a transaction and successfully places it in the extracted block, it is considered a verified transaction. Each block can only hold a limited number of transactions, which is currently an average of 2,500 transactions. In cases where network traffic is high, and many transactions are awaiting approval, the priority of miners is with a transaction for which a higher fee is provided.
Fees can determine the urgency of your transaction. In fact, if you want your transaction to be at the forefront of the verification queue, you have to pay a higher fee to the miners. If time is not important to you, you can use a lower fee. Also, note that the sender of the transaction always pays the fees.
Now we will explain more about the question of how to determine the standard fee for bitcoin transactions.
How to determine fees in bitcoin transactions
To better understand how to set fees on bitcoin transactions, it is best to review a few simple concepts.
UTXO The bitcoin
the system works, unlike banks. In banks, to determine how much balance each person has, a list of users’ balances is available to the bank, which reduces one person’s balance at the transaction time and adds it to another person’s balance. But there is no such mechanism in Bitcoin, and there is no list of used inventory. Bitcoin uses the UTXO model instead of the need to store each user’s inventory directly.
In UTXO models, the network determines whether you have enough assets to complete the transaction based on all the transactions you have received or sent in your wallet.
To better understand this concept, consider this example:
Suppose you have 75,000 tomans in cash in your wallet. Since we do not have 75,000 Toman banknotes, there is a combination of different banknotes in your wallet, which adds up to a total of 75,000 Tomans.
Think of each banknote as an unspent output. Each banknote has a value that you can use in your next exchanges.
Now let’s take this example one step further. Suppose you want to buy lunch for 28,000 tomans out of 75,000 tomans. To buy lunch, you have to give the restaurant a few bills (unspent transaction output) pay for lunch. Suppose that your 75,000 Tomans includes seven 10,000 Toman banknotes and one 5,000 Toman banknote.
So, in general, you have 8 unused transaction outputs (UTXO). Now, to buy a 28,000 Toman lunch, you pay three UTXO (three 10,000 Toman banknotes), and the restaurant returns two thousand Toman.
Therefore, consider the three 10,000 Toman banknotes you paid as UTXO, which will be spent and will no longer be considered unspent. Consider the other two thousand tomans as a UTXO that will be returned to you.
Now let’s get out of the fictional example and look at a real example:
When someone wants to send you 1.2 bitcoins, they must have UTXO in their wallet (the user does not need to do anything) equal to the value of the amount sent. Suppose the person in question has two unspent outputs in his wallet, one worth one bitcoin and the other is worth 0.5 bitcoins. So the person we are looking for has 1.5 UTXO bitcoins in his wallet, but he wants to send you 1.2. So when he sends the transaction, he is actually telling the network that I am sending a total of 1.5 bitcoins, and you have to give 1.2 bitcoins to the recipient and return the other 0.3 bitcoins to my address.
In other words, when you want to send money to a network that includes a group of miners and nodes, you show your previous transactions and say that these are proof of bitcoin. Then your transaction is recognized as valid and enters the block.
To summarize, we can say:
The term UTXO means “unspent transaction output.” Simply put, each UTXO acts like a cash note that stores value (in the form of bitcoin) and can only be spent once. So every bitcoin transaction consumes (at least) one UTXO and creates one or more new UTXOs.
Transaction input
Each bitcoin network transaction uses one or more UTXOs (unspent output of previous transactions) as the transaction input. Depending on the transaction amount, the sender selects the appropriate input from the UTXOs in his wallet.
Transaction
outputs Transaction outputs determine the destination of incoming bitcoins. Each output specifies how many of the incoming bitcoins will be transferred to what address. Transaction outputs eventually generate stand-alone UTXOs, each of which can be spent separately.
To better understand how the above components work, see the example below.
How to use UTXOs and determine the input and output of transactions
The example above shows how to use UTXOs and configure transaction inputs and outputs. But if we consider these two transactions to be real, no miner will approve them; Because in these transactions, no share is considered a commission.
Now that we know the basics of bitcoin transactions, we can provide a more accurate definition of commission:
Bitcoin transaction fees are a type of output that determines that part of the transaction amount is transferred as a fee to the miner’s address who confirms the transaction. Therefore, the transaction’s sender determines the amount of the commission through his wallet and leaves the output address of the commission blank. Any miners trying to verify this transaction and register it in the block can put their wallet address in this blank. But in the end, only a miner succeeds in receiving the transaction fee that can record this transaction in one block.
Now the question is, how do we set a fee in a real transaction?
All we have said so far is a mechanism behind the scenes of bitcoin transactions. But in reality, you do not need to bother to send a transaction from the wallet. To send a transaction, enter the amount and address of the recipient in your wallet.
Today’s wallets automatically select the appropriate inputs for the transaction and set the transaction fee based on the average current network fees. But with the help of the following methods, you can manage and reduce your transaction fees.
The bitcoin transaction fee is fundamentally different from the fiat money transaction fee. When you work with Fiat money, the transaction fee depends directly on the transaction amount; That is, as the transaction amount increases, the commission will also increase; But in the Bitcoin network, the amount of the transaction has nothing to do with the commission and the only factor influencing the commission is the size of the transaction.
Because the larger the transaction size (i.e., the total number of inputs and outputs), the more complex and difficult it will be to validate and verify.
Therefore, miners prioritize transactions in the ampoule based on the Fee Rate.
The bitcoin transaction fee is expressed in satoshi per byte (sat/byte). In other words, the commission rate indicates that you want to pay a few satoshis per byte of your transaction.
Select the appropriate fee for the transaction
To choose the best rate, you can go to the website bitcoinfees.earn.com See. On this website, pending transactions in the package, along with the fee rate and the estimated time of their approval, are specified and updated instantly.
So depending on the priority and importance of your transaction, you can determine the appropriate fee rate. Note that the fee rate can vary depending on the amount of network traffic at any given time. As shown below, when the network is not busy, you can pay 1Satoshi Confirm your transaction for each byte.
Click on the image to view the full size.
Satoshi is the smallest unit recorded in the Bitcoin blockchain: one Satoshi means one point, seven zeros, and one. In other words, a Satoshi is equal to: 0.00000000001 bitcoin or 8–10 * 1.0 BTC.
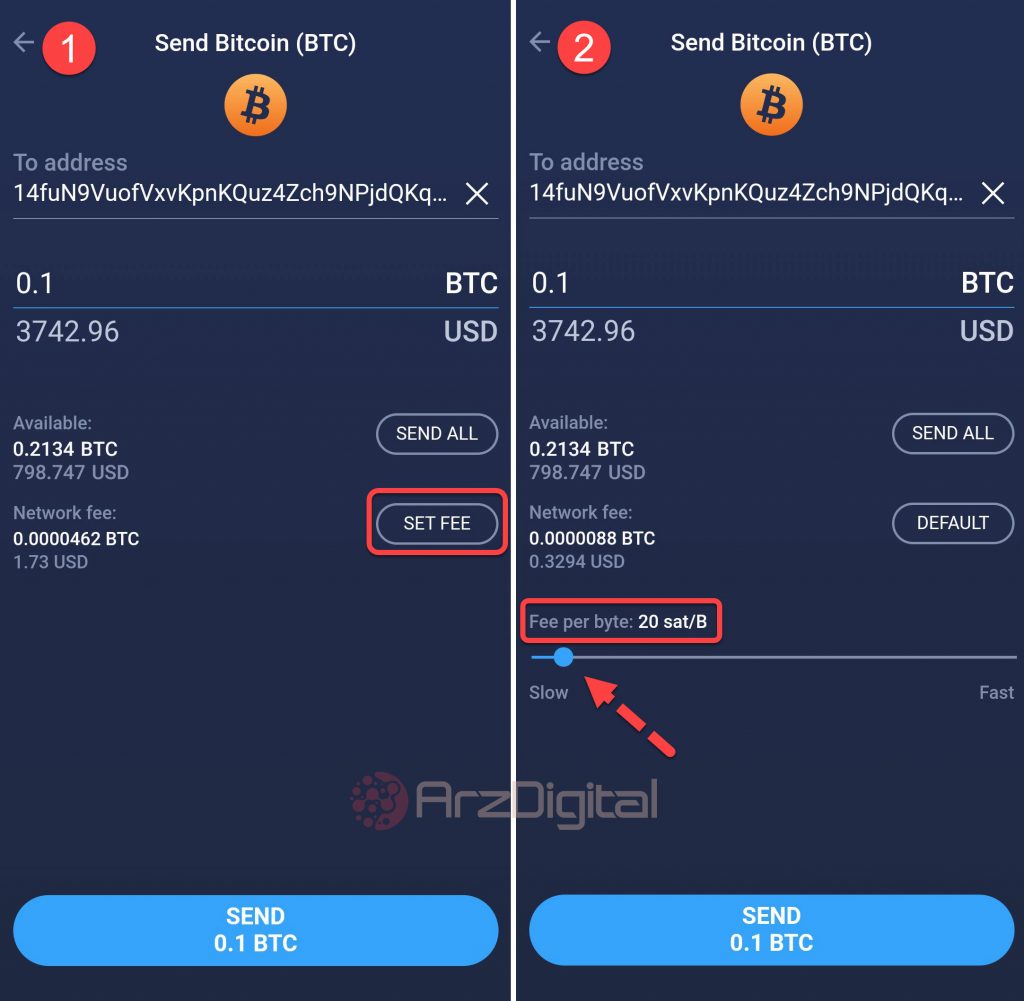
Change the fee rate in the wallet.
Bitcoin wallets work in such a way that they offer a reasonable fee to their users based on current and recent network activities. However, some of these wallets and services do not work properly in calculating the fee and demand more fees from their users. The impact of this issue is not limited to the users of these wallets and also affects the overall network fee rate.
Most wallets allow you to set your transaction fees manually or set at least one general priority (low, medium, or high) for your payment fee. So after you choose the right fee for the transaction, you have to enter it into your wallet.
The image below shows how to change the fee in the wallet Atomic You see.
How are commissions displayed in the China block?
In general, to access bitcoin blockchain information, you must use blockchain proxies such as blockchair.com Or blockchain.comTo use. These platforms specify transaction hashes, transaction inputs, outputs, and details such as transaction size, commission, and transaction confirmation time.
But the Bitcoin blockchain does not list the fees paid for each transaction separately. The only way to determine the amount of commission paid by the sender is to calculate the difference between the number of bitcoins sent (i.e., the sum of transaction inputs), the number of bitcoins received, and the number of bitcoins returned (as the remainder of the transaction) returned to the sender.

Several ways to reduce bitcoin transaction fees

There are several ways you can reduce your transaction fee. In this section, we will look at some of the best ways to reduce bitcoin transaction fees:
1. Do not transact when network traffic is high
When the bitcoin network is overcrowded (for example, when prices are rising and many people are looking to buy bitcoins), users often increase their transaction fees to prioritize their transactions. To be placed.
This can irrationally increase transaction fees. So if you can postpone your transaction until the network becomes more secluded, you will not have to pay astronomical fees.
2. Use Segwit wallets
(SegWit), Segregated Witness is one of the Bitcoin network updates that greatly reduces the size of the transaction information by using its unique design to arrange the transaction information. Many bitcoin wallets now support this feature, which reduces transaction fees by a fraction.
3. Merge
Inputs The more inputs needed to create your transaction, the larger the transaction size, and as a result, you will have to pay a higher fee to do so. You can merge your inputs from time to time to reduce costs.
Merge inputs mean that when the network is secluded (and fees are low), you can send your various inputs to an address you own, which is called a “consolidation transaction.” That way, you’ll only have one entry, and your transaction fee will be significantly lower in the future. One of the wallets that allow users to view and manage all texts is the wallet electrum Is.
4. Group outputs
In addition to merging inputs, you can also place several different outputs (or payments) in one transaction. Of course, not all wallets support this feature; But if your wallet has this feature, you can send your payments in the form of a grouped transaction to several different addresses for a lower fee. One of the best wallets for this is the Electrum wallet.
5. Use the
Lightning is a second-tier solution for the Bitcoin network that allows you to perform day-to-day transactions offline. In the Lightning network, people can make their exchanges instantly and indefinitely by creating a “payment channel” with others and entering a certain amount of bitcoin into the channels in pairs (P2P). To use the Lightning feature, you must use special wallets such as Blue wallet or Bitcoin lightning wallet.
Common Questions
Here are some of the most commonly asked questions about Bitcoin fees and answers.
Why is my bitcoin transaction not approved for a long time?
Although reading this guide (and the like) sheds light on some of the fee issues, most Bitcoin users are still not experts in this area. Therefore, many times (especially when the price is on the rise and the network traffic is high), there are complaints from users of this network that they are “not approved” or “levitating. We hear transactions.
But, what causes transactions to be not approved or suspended?
The non-approval of transactions for a long time is probably due to one of two reasons:
1. The fee you paid was not high enough; Therefore, miners prefer to process other transactions to your transaction.
2. You are sending recently received coins; While the transaction of sending these coins to you has not yet received sufficient verifications in the China block and has not been finalized (some wallets also show transactions that have been sent to you but have not yet been verified by network members).
What has he done to you in this situation?
Method 1: Wait
Sometimes waiting is the best thing you can do. If your transaction is not urgent and you are not in a hurry to do it, it is better to forget it for at least 72 hours. After this time, the task of this transaction will finally be determined; That is, it is either approved or canceled and returned to your wallet.
Second method: use the “wage replacement.”
Replacement fees or RBF (Replace By Fee) is a unique feature that allows the transaction wallet with higher fees back to the network. This will confirm the transaction with a higher fee, and the transaction with a lower fee will be considered invalid. Keep in mind that only a handful of wallets support a fee replacement feature, and in some wallets, a fee replacement is an optional feature.
If your wallet supports this feature, you will easily get rid of the hassle of transaction fees. It should be noted that replacing the fee (with a higher amount) does not pose any problems or risks to your transaction. Electrum wallets and Walt Samurai (Samourai Wallet) are two of the best wallets that support RBF capability.
Method 3: Transaction
Accelerators various transaction accelerators are operated by extraction pools. These accelerators cause (under certain conditions) your transaction to be placed in the next block.
Some of them are free; While others have certain restrictions on the size of the transaction. Some pools also charge a fee for doing this before extraction; Others receive this fee as a reward during the transaction.
You need your transaction ID (tx id) to place your transaction in an accelerator. This unique identifier represents your transaction and is usually found in the list of transactions in your wallet.

Some of the best transaction accelerators available include:
- accelerator Coolwave Which is a good option for unapproved and suspended transactions. To use this accelerator, you must first create an account in the BitcoinTalk community.
- Accelerator ViaBTC is free but often not available; it only accepts 100 unapproved transactions per hour. Therefore, if you intend to place your transaction in this accelerator, you must send your request to accept your transaction ID at the beginning of each hour and repeatedly. Of course, ViaBTC has another version that helps process the transaction for a fee; But the cost of this special option is only in the templateBitcoin Cache Accepts. In the image below, you can see the ViaBTC Accelerator page.

Method 4: Spend twice (last resort)
Spend twice(Double-spending) is a method in which we repeat an unverified transaction (with the same inputs and different outputs) and send it back to the network. In fact, in the repurchase method, we try to motivate the miners to approve the second transaction earlier than the original transaction. Thus the initial transaction (because its inputs have been spent once in the Chinese block) will no longer be approved.
In fact, this solution is very similar to a fee replacement; But with one major difference: the fee replacement method is following the rules set out in the Bitcoin Protocol, and for this reason, you can access it in some Bitcoin wallets; But the double-spending method is against the Bitcoin protocol rules, and therefore, this feature is not available in regular wallets. Double spending is one of the major problems that Bitcoin was created to solve, and all official Bitcoin wallets are designed to prevent it.
Method 5: Paying the CPFP fee (last)
resort ) CPFP stands for Child Pays for Parent and literally means “paying the child for the parent.” In fact, in this method, the “child transaction” (second transaction) created after the “parent transaction” (first transaction) can pay the fee required to confirm the initial transaction. In the CPFP method, you spend coins that are input but have not yet been verified; That is exactly what we forbade to do before.
Basically, the idea of the CPFP method is that the fee for new outbound transactions will be high enough to be sufficient both for itself and for the unapproved incoming transactions to which it depends.
Because it is impossible to process a new transaction before confirming an old transaction, miners are encouraged to process the (original) parent transaction first to obtain the child transaction fee (which is higher and sufficient for both transactions).
Both of the above methods (double-spending and CPFP) are very difficult to do and may put your assets at risk. In fact, these methods are not recommended for ordinary users, so we will not go into more detail about them in this guide.
Could my bitcoin transaction be suspended forever?
- Short answer: No.
- Correct Answer: Probably not, but it depends. In the first part of this article, we talked about the waiting queue for transactions in the memory pool to be selected by miners.
The point is, a memory pool is not limited to one location. Each computer (or node) that approves transactions has a partition on its hard disk dedicated to storing pending transactions. Therefore, different nodes have different versions of the memory pool, depending on what transactions they know or remember.
If a transaction is not approved for a long period of time, it will eventually be removed from the node memory pool.
The default time for deleting unapproved transactions is 72 hours, But the nodes may change this time at will.
Also, with the introduction of higher fee transactions and due to the limited capacity of memory pools, less valuable transactions may be eliminated from these pools.
Because of this, a 72-hour wait is likely to have one of two consequences: Your transaction will either be approved or removed from all network memory pools, and the assets will be returned to your wallet.
However, a node may never forget your transaction and occasionally replay it on the network and remind other nodes. In this case, your transaction may be suspended forever.
Is sending bitcoins free?
No. Wage laws were different in the past than they are today. If your transaction was small enough or had priority, you could even submit your transactions for free. But today, every bitcoin transaction requires a minimum amount of commission to be approved.
Who receives the Bitcoin transaction fee?
The bitcoin transaction fee is paid to the miner who successfully placed the approved transaction in the newly extracted block.
Why are Bitcoin fees so high?
When many people are sending bitcoins, a queue of unapproved transactions is formed. People who want to process their transactions faster will pay a higher fee for their transactions. This issue creates a competition called “fee war” between participants who want to confirm their transaction as soon as possible.
However, sending bitcoins becomes much cheaper when the network is relatively secluded.
How much does Bitcoin charge per transaction?
To calculate the appropriate commission for each transaction, you must multiply the size of your transaction (shown on most Bitcoin wallets) by the set commission rate. Of course, finding the current network rate is not a difficult task, and we have already introduced websites that can help you with this.
Is it possible to reduce the withdrawal fee from an exchange office?
When you withdraw bitcoins from your account in digital currency exchanges, it is actually the exchange that transacts from your internal wallet. In other words, even though you own the bitcoins, here the money changer is the sender, and you are the receiver.
Therefore, in such cases, you can not change the withdrawal fee from the exchange. Exchange offices usually set the withdrawal fee so that the transaction is done at a standard speed.
This is why you often find that the withdrawal fee from the exchange offices is higher than the transaction fee in your personal wallet. Some exchanges may charge you more than the network fee, and the user does not have to do anything special.
Conclusion
As you can read, the issue of fees is very complex and can pose many challenges. In fact, the main reason for creating Fork The bitcoin cache of the bitcoin network was to increase the capacity and size of bitcoin blocks. The size of bitcoin blocks limits the number of transactions that the network can process and verify per block. This will increase the number of pending transactions and, consequently, the fees for these transactions.
Low fees in the Bitcoin network are significant; Because the creation of a cheap and peer-to-peer payment system was one of the most important goals on which Bitcoin was based.
However, as usual, in addition to low fees, other considerations such as network security must be considered.
As bitcoin grows in popularity, more and more people are turning to it, and the bitcoin network needs to find new ways to address this growing demand—one of the most promising solutions now, Lightning Network (Lightning Network).
Although the Lightning network is not yet fully ready for widespread use, its use (shortly) could instantly free Bitcoin users.